Office Ergonomics
What’s Ergonomics?
Ergonomics is the science of designing and arranging workplaces, products, and systems to fit the people who use them, optimizing their well-being and overall performance.
Ergonomic Risk Factors
-
Awkward Postures:
-
Reaching, bending, twisting, or holding body parts in unnatural positions for extended periods
-
Examples include bending over to pick up objects, reaching for items on high shelves, or twisting to access equipment.
-
Poor posture while sitting or standing can also be a risk factor.
-
-
Force and vibration:
-
Applying excessive force to perform tasks, such as lifting heavy objects, pushing or pulling carts, or gripping tools tightly.
-
Heavy lifting, especially with improper technique, is a significant risk factor.
-
Exposure to vibration from tools or equipment.
-
Examples include using power tools, operating machinery, or driving vehicles.
-
-
Repetition:
-
Performing the same motions repeatedly, like typing, using a mouse, or assembling parts.
-
-
Contact Stress:
-
Direct pressure on the body from hard surfaces or edges, such as resting the wrist on the edge of a desk.
-
-
Static Postures:
-
Maintaining the same position for extended periods, such as sitting at a desk without breaks.
-
Reducing Office Ergonomics Risk Factors
-
Awkward Posture:
Adjust chair height, monitor position, keyboard & mouse placement and desk height
-
Force and vibration:
Use appropriate size equipment and tools. Apply proper lifting techniques.
-
Repetition motions:
Take frequent breaks and alter tasks.
-
Contact stress:
Use wrist and arm support
-
Static postures:
Take breaks and alter position to reduce duration in static/fixed position

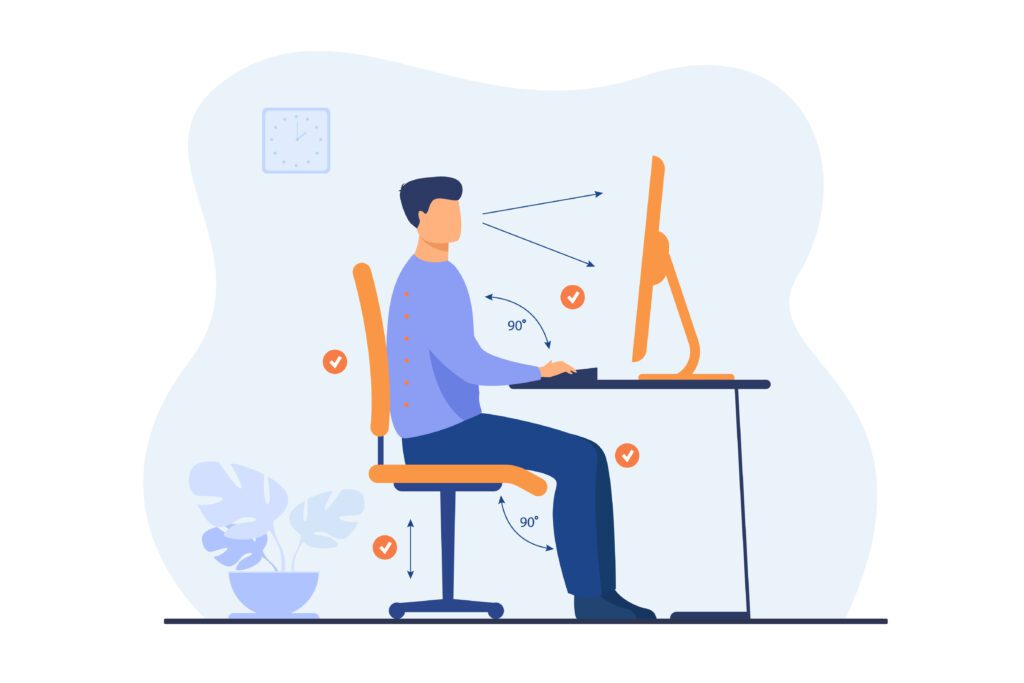
Ergonomic Office Workstation Setup
Feet to the Floor
-
Feet should be flat on the floor or on a footrest if necessary
-
Chair height should allow your legs to be in a neutral posture with knees level with hips or slightly below
Body to chair
-
The seat pan should be adjusted correctly to allow for the space of two fingers between the back of your legs and the chair
Desk and input devices
-
Desk height should allow for elbows to rest at bellybutton height
-
Input devices should be placed next to each other
-
Use a mouse that promotes a neutral or handshake wrist posture
-
Wrists should rest in either a neutral or slight negative tilt position
-
Wrist support should be used to reduce contact stress
Monitor(s)
-
Eyes should rest comfortably at the top 1/3 of the screen, promoting the neck to be in a neutral posture
-
Monitors should be an arm’s length distance away
-
If using two monitors equally center yourself. If using one monitor more often center yourself on the main monitor.